- American Bio Labs
- American Funded Bio Labs
- American Weapons of Mass Destruction
- Biden Crime Family
- Biden Regime
- Bio Weapons
- Biolabs in Ukraine
- Capitol Hill
- China Government
- China News
- Chinese Communist Party
- Chinese Global Activities
- Coming Economic Collapse
- Conservative Daily Thoughts
- Constitutional Threat
- Corona Virus
- Covid-19
- Covid-19 Pandemic
- Declassified Info
- Democrat Lies
- Democrat Party
- DNC
- Dr. Fauci
- Election Fraud
- Global Criminals
- Global Pandemic
- Global Pandemics
- Global Threat
- Government Corruption
- Governmental Abuse
- Imminent Threat
- Impeachment of Joe Biden
- Lying Fact-Checkers
- National Emergency
- National News Bias
- News of the Day
- NWO
- Republican News
- Republican Party
- Republicans
- RINOS
- RNC
- Socialism in America
- Supply Chains
- Supreme Court's Failure to Act
- Theron News Press
- Top Media Videos
- Trump News
- US Fraudulent Elections
- Weapons of Mass Destruction
- WHO
- Wuhan Bioweapons Lab
- Wuhan Lab in China
- Wuhan Lab paid for by Dr. Fauchi
- Wuhan Virus
Global origins of Covid-19 and the virus origins that killed over 6.8 million humans
7 min read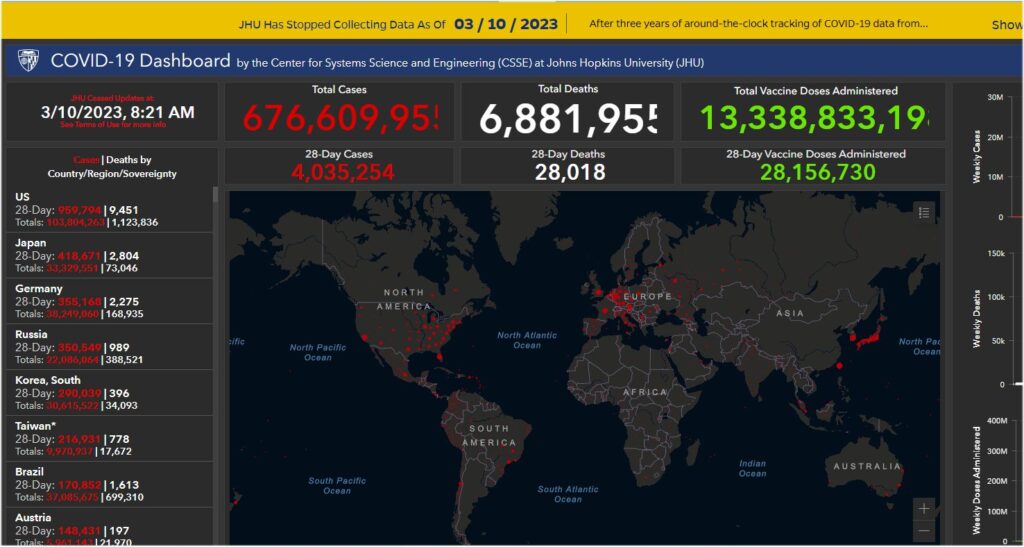
As usual in the Congressional inquiry, Republicans that are slow on the uptake of the criminality of the democRAT party are doing the investigation. And as usual, democRATS are blaming the questioning of the origins by Republicans as pure “white supremacy” or “extreme partisanship”.
The question still remains, why was Obama in 2015 visiting the Wuhan Lab with Dr. Fauchi? Why were Fauchi, the Department of State, and the DOD involved in this funding?
Gain-of-Function research is illegal worldwide.
The United States is reported to have 336 bio-labs in 30 countries, including 48 in Ukraine. Media reports also say that the research the biological laboratories funded and controlled by the US in Ukraine conducted could be behind the increase in the number of cases of diphtheria, rubella, tuberculosis and measles in the country since 2014. Besides, the World Health Organization has included Ukraine in the list of countries with a high risk of a polio outbreak.
The Russian Defense Ministry claims the documents it has acquired from the personnel of a bio-lab in Ukraine show that the US and its NATO allies have been conducting research on biological weapons, including the highly infectious bird flu virus which spreads through migratory birds, and pathogens such as bacteria and viruses that can be transmitted from bats to humans.
The bio-labs in Ukraine, according to some reports, have been working to develop components of biological weapons, just like what Japan’s Unit 731 did before and during World War II.
Japan’s use of chemical and biological weapons in China caused the deaths of about 1.2 million Chinese people between 1932 and 1945. The US acquired and utilized the research materials and personnel of Japan’s Unit 731, and used such weapons in Korea (during the Korean War-1950-53), Vietnam, the Middle East and Kosovo, poisoning and killing millions of people after World War II.
The international community reached a consensus on banning the use of biological weapons after World War I, during which Germany, the United Kingdom and France used such weapons, leading to heavy casualties. The ban was reinforced in 1972 and 1992 with the prohibition on the development, production, stockpiling and transfer of biological weapons.
The 1925 Geneva Protocol is the first international pact that banned the use of asphyxiating, poisonous and other gases, and bacteriological weapons in war. The Biological Weapons Convention or the Biological and Toxin Weapons Convention of 1972 moved further toward the total elimination of such weapons by prohibiting their development, production, stockpiling, acquisition, retention, transfer, and their delivery systems, as well as requiring their destruction.
The BTWC supplements the 1925 Geneva Protocol. And the Chemical Weapons Convention, concluded in 1992, extended the prohibition to the development, production, stockpiling, retention and transfer of chemical weapons, and their delivery systems. The CWC also requires such weapons to be destroyed.
And the US has ratified all these conventions and agreements.
The US military’s bioresearch in Ukraine and other countries violates the 1925 Geneva Protocol and the BTWC, which are an important part of the international law to prevent the proliferation of weapons of mass destruction. And as a pillar of international peace and security, the BTWC has the support of an overwhelming majority of the countries in the world.
The state parties to the BTWC have ensured that it remains effective and is continuously strengthened. However, the US refuses to allow international monitoring of its weapons research facilities, and has not stopped research into biological and chemical weapons. In 2001, the US unilaterally withdrew from the negotiations on the development of an additional protocol to the BTWC, according to which an independent body, the “Technical Secretariat”, was supposed to monitor the microbiological research activities of all countries.
The US military used on its own territory a combat biological formulation of anthrax strain, Ames strain, resistant to all antibiotics and not amenable to treatment, according to the Russian Academy of Sciences. Worse, the US has been blocking the establishment of the BTWC’s verification mechanism for more than 20 years.
It is clear therefore that the US resorts to double standard on bioresearch, as it does on many other issues of global concern. And yet it made outlandish accusations against China that the novel coronavirus had leaked from the Wuhan Institute of Virology without providing any evidence.
Moreover, US President Joe Biden ordered a 90-day review by US intelligence agencies even after the WHO report on COVID-19 concluded that a lab leak was “extremely unlikely”. On the other hand, the US has not accepted an international investigation into Fort Detrick, a US military lab where research on coronaviruses had been going on for years.
In July 2019, the US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention ordered a halt in research work at Fort Detrick in Maryland after a respiratory disease of unknown causes broke out in a community near the lab and several thousand cases of pneumonia with symptoms similar to those of COVID-19 were reported in several states in the US.
Global Law – BTWC

Biological weapons disseminate disease-causing organisms or toxins to harm or kill humans, animals or plants. They can be deadly and highly contagious. Diseases caused by such weapons would not confine themselves to national borders and could spread rapidly around the world. The consequences of the deliberate release of biological agents or toxins by state or non-state actors could be dramatic. In addition to the tragic loss of lives, such events could cause food shortages, environmental catastrophes, devastating economic loss, and widespread illness, fear and mistrust among the public.
The Biological Weapons Convention
The Biological Weapons Convention (BWC) effectively prohibits the development, production, acquisition, transfer, stockpiling and use of biological and toxin weapons. It was the first multilateral disarmament treaty banning an entire category of weapons of mass destruction (WMD).
The BWC is a key element in the international community’s efforts to address WMD proliferation and it has established a strong norm against biological weapons. The Convention has reached almost universal membership with 185 States Parties and four Signatory States.
Text of the Convention
The BWC itself is comparatively short, comprising only 15 articles. Over the years, it has been supplemented by a series of additional understandings reached subsequent Review Conferences. The BWC Implementation Support Unit regularly updates a document that provides information on additional agreements which (a) interpret, define or elaborate the meaning or scope of a provision of the Convention; or (b) provide instructions, guidelines, or recommendations on how a provision should be implemented.
Formally known as “The Convention on the Prohibition of the Development, Production and Stockpiling of Bacteriological (Biological) and Toxin Weapons and on their Destruction”, the Convention was negotiated by the Conference of the Committee on Disarmament in Geneva, Switzerland. It opened for signature on 10 April 1972 and entered into force on 26 March 1975. The BWC supplements the 1925 Geneva Protocol, which had prohibited only the use of biological weapons.
States Parties to the Biological Weapons Convention undertook “never in any circumstances to develop, produce, stockpile or otherwise acquire or retain:
- microbial or other biological agents, or toxins whatever their origin or method of production, of types and in quantities that have no justification for prophylactic, protective or other peaceful purposes;
- weapons, equipment or means of delivery designed to use such agents or toxins for hostile purposes or in armed conflict.”
BWC States Parties have strived to ensure that the Convention remains relevant and effective, despite the changes in science and technology, politics and security since it entered into force. Throughout the intervening years, States Parties have met approximately every five years to review the operation of the BWC. Between these Review Conferences, States Parties have pursued various activities and initiatives to strengthen the effectiveness and improve the implementation of the Convention. A total of eight Review Conferences have taken place since the first one in 1980.
Key Provisions of the Convention
|
Article |
Provision |
|
Article I |
Undertaking never under any circumstances to develop, produce, stockpile, acquire or retain biological weapons.
|
|
Article II |
Undertaking to destroy biological weapons or divert them to peaceful purposes.
|
|
Article III |
Undertaking not to transfer, or in any way assist, encourage or induce anyone to manufacture or otherwise acquire biological weapons.
|
|
Article IV |
Requirement to take any national measures necessary to prohibit and prevent the development, production, stockpiling, acquisition or retention of biological weapons within a State’s territory, under its jurisdiction, or under its control.
|
|
Article V |
Undertaking to consult bilaterally and multilaterally and cooperate in solving any problems which may arise in relation to the objective, or in the application, of the BWC.
|
|
Article VI |
Right to request the United Nations Security Council to investigate alleged breaches of the BWC, and undertaking to cooperate in carrying out any investigation initiated by the Security Council.
|
|
Article VII |
Undertaking to assist any State Party exposed to danger as a result of a violation of the BWC.
|
|
Article X |
Undertaking to facilitate, and have the right to participate in, the fullest possible exchange of equipment, materials and information for peaceful purposes.
|
Further information, including information on adherence, can be found in the UNODA Disarmament Treaties Database.